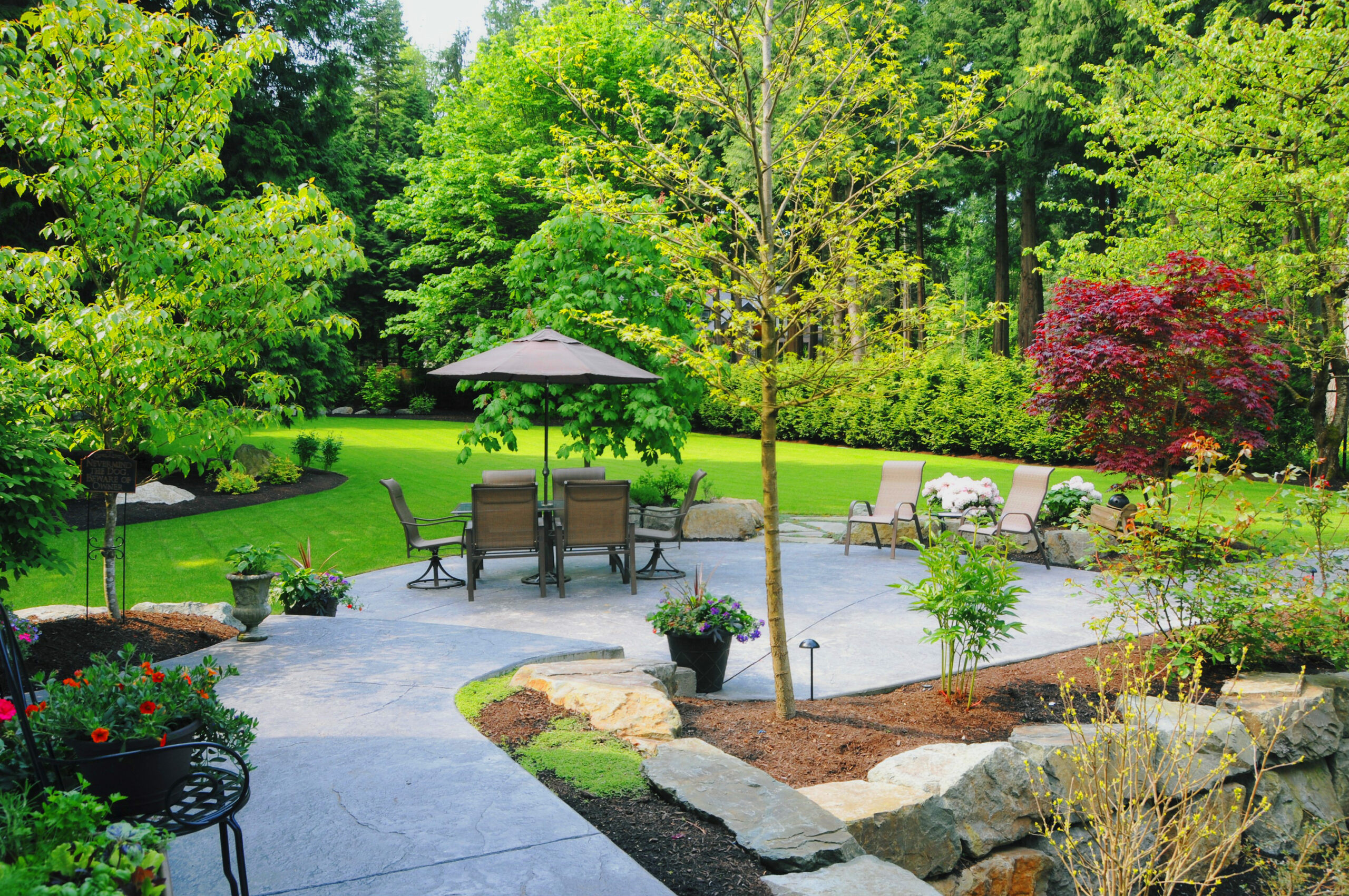
In today’s world, sustainability is no longer a luxury but a necessity. As urbanization continues to grow, natural landscapes are being replaced by man-made environments, leading to a loss of biodiversity and an increased strain on natural resources. Sustainable landscaping, a thoughtful approach to designing and managing outdoor spaces, addresses these challenges by blending ecological responsibility with human needs. It focuses on creating outdoor areas that are not only visually appealing but also environmentally friendly, resource-efficient, and supportive of local ecosystems.
This article explores the concept of sustainable landscaping in depth, shedding light on its principles, benefits, and implementation while addressing the challenges and future prospects of eco-friendly outdoor spaces.
What Is Sustainable Landscaping?
Sustainable landscaping is a holistic approach to creating outdoor spaces that work in harmony with the environment. Unlike traditional landscaping, which often prioritizes aesthetics over environmental impact, sustainable landscaping considers the long-term health of ecosystems. This means using practices that conserve resources like water and energy, protect soil health, and reduce pollution.
For instance, a traditional landscape may involve extensive irrigation, chemical fertilizers, and plants that are not suited to the local climate. These practices, while effective in creating a lush appearance, can deplete natural resources and harm the environment. In contrast, sustainable landscaping focuses on using native plants, reducing water consumption, and implementing eco-friendly materials and techniques.
Why Is It Important?
- Environmental Health: Conventional landscaping practices often lead to water wastage, soil erosion, and pollution. Sustainable landscaping minimizes these impacts, preserving the environment for future generations.
- Resource Efficiency: By reducing dependency on external resources like chemical fertilizers and excess water, sustainable landscaping lowers costs and conserves vital resources.
- Resilience to Climate Change: Eco-friendly landscapes are better equipped to withstand extreme weather conditions, such as droughts or heavy rainfall, making them a practical solution in a changing climate.
Principles of Sustainable Landscaping
Sustainable landscaping is guided by several principles, each focusing on a different aspect of environmental stewardship and resource management. Below are detailed explanations of these core principles:
1. Water Conservation
Water is a precious resource, yet traditional landscaping often requires large quantities for irrigation. Sustainable landscaping seeks to minimize water use through several strategies:
- Drip Irrigation: Unlike sprinkler systems that spray water indiscriminately, drip irrigation delivers water directly to the roots of plants. This method significantly reduces evaporation and ensures that plants receive water where they need it most.
- Rainwater Harvesting: This involves capturing rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces and storing it for irrigation. Rainwater harvesting reduces reliance on municipal water systems and prevents water runoff, which can cause erosion.
- Drought-Tolerant Plants: Choosing plants that thrive in dry conditions eliminates the need for frequent watering, especially in arid regions.
These methods not only conserve water but also reduce costs and encourage responsible water use.
2. Planting Native and Adaptive Species
Native plants are those that naturally occur in a particular region. They are adapted to the local climate, soil conditions, and ecosystems, which means they require minimal maintenance and resources. For example:
- Low Water Needs: Native plants are accustomed to local rainfall patterns, reducing the need for supplemental irrigation.
- Biodiversity Support: They provide food and shelter for native wildlife, including pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds.
- Pest Resistance: Native plants are less susceptible to local pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Adaptive species, which are non-native plants capable of thriving without disrupting local ecosystems, can also be included in sustainable landscaping.
3. Soil Health Management
Healthy soil is the cornerstone of a sustainable landscape. Practices like excessive tilling, chemical fertilizers, and erosion can degrade soil quality over time. Sustainable landscaping focuses on:
- Composting: Adding organic matter to the soil improves its fertility and structure. Kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials can be composted to create a nutrient-rich amendment.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of mulch around plants helps retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and suppress weeds. Mulch also breaks down over time, enriching the soil.
- Avoiding Chemicals: Natural fertilizers, such as bone meal or fish emulsion, provide essential nutrients without harming soil microorganisms.
4. Energy Efficiency
Landscapes can significantly impact energy consumption, particularly in urban settings. Sustainable landscaping incorporates features that reduce energy use, such as:
- Shade Trees: Strategically planting trees can lower cooling costs by shading buildings during summer.
- Windbreaks: Dense hedges or rows of trees can reduce heating costs by blocking cold winds in winter.
- Solar Lighting: Solar-powered outdoor lights eliminate the need for electrical wiring and reduce energy bills.
These measures enhance the functionality of outdoor spaces while reducing environmental impact.
5. Reduction of Waste
Waste is a major issue in landscaping, but sustainable practices aim to minimize it at every stage:
- Recycling Materials: Hardscaping elements like stones, bricks, and wood can be reused in new designs. For example, old concrete slabs can be crushed and used as gravel for pathways.
- Composting Organic Waste: Grass clippings, leaves, and plant trimmings can be composted instead of being discarded. This reduces landfill waste and provides valuable nutrients for soil.
- Upcycling: Creative reuse of materials, such as turning an old barrel into a rainwater collection system or using reclaimed wood for garden beds, adds character to the landscape while reducing waste.
Designing Sustainable Outdoor Spaces
Creating a sustainable landscape involves thoughtful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step approach to designing an eco-friendly outdoor space:
Step 1: Conduct a Site Analysis
Understanding the unique characteristics of your site is crucial. This includes assessing:
- Soil Type: Knowing whether the soil is sandy, clayey, or loamy helps determine which plants will thrive.
- Sunlight Patterns: Identifying sunny and shady areas ensures plants are placed where they’ll grow best.
- Water Drainage: Observing how water flows during rain can inform the placement of features like rain gardens or swales.
Step 2: Set Clear Objectives
What do you want your landscape to achieve? Your goals might include:
- Reducing water use.
- Creating a space for relaxation and recreation.
- Attracting pollinators and other wildlife.
Clear objectives will guide your design choices.
Step 3: Prioritize Native and Drought-Resistant Plants
Choose plants that are well-suited to your local conditions. Grouping plants with similar water and sunlight needs makes irrigation and maintenance more efficient.
Step 4: Integrate Functional Features
Incorporate eco-friendly elements that enhance usability and sustainability, such as:
- Permeable paths made of gravel or porous pavers.
- Rain gardens to capture and filter stormwater.
- Edible plants, like herbs and vegetables, which provide fresh produce.
Step 5: Minimize Resource Use
Opt for low-maintenance designs that reduce dependency on water, fertilizers, and energy. For instance, replace traditional lawns with ground covers like clover or moss.
The Benefits of Sustainable Landscaping
Environmental Benefits
- Conservation of Resources: Sustainable landscapes require less water, energy, and chemicals.
- Biodiversity Support: Native plants and wildlife-friendly features encourage diverse ecosystems.
- Improved Soil Health: Organic practices restore soil fertility and prevent degradation.
Economic Benefits
- Cost Savings: Reduced water and energy usage lowers utility bills. Native plants and low-maintenance designs cut long-term maintenance costs.
- Increased Property Value: Eco-friendly landscapes are attractive to potential buyers and can boost property values.
Social and Psychological Benefits
- Enhanced Well-Being: Green spaces are known to reduce stress, improve mental health, and foster a sense of connection with nature.
- Community Engagement: Shared gardening or sustainable landscaping projects can strengthen community bonds.
The Future of Sustainable Landscaping
As environmental awareness grows, sustainable landscaping is becoming more mainstream. Emerging trends and technologies, such as vertical gardens, green roofs, and smart irrigation systems, are making it easier to create eco-friendly outdoor spaces. Cities are increasingly incorporating green infrastructure into urban planning to mitigate climate change impacts and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Sustainable landscaping is more than a design trend—it’s a necessary shift toward environmental responsibility and resource conservation. By embracing principles like water conservation, native planting, and waste reduction, we can create outdoor spaces that are not only beautiful but also beneficial to the planet. Whether for a small backyard or a large urban park, sustainable landscaping offers a blueprint for building a greener, healthier future.